planar_convergence¶
The planar_convergence test group implements convergence studies for
doubly periodic, planar meshes. Currently, the only test case is the
horizontal advection of a Gaussian tracer.
resolutions¶
To alter the resolutions used in this test, you will need to create your own
config file (or add a planar_convergence section to a config file if you’re
already using one). The resolutions are a comma-separated list of the
uniform resolution of the mesh in km. If you specify a different list
before setting up horizontal_advection, steps will be generated with the
requested resolutions. (If you alter resolutions in the test case’s config
file in the work directory, nothing will happen.)
time step¶
The time step for forward integration is determined by multiplying the
resolution by dt_1km, so that coarser meshes have longer time steps.
You can alter this before setup (in a user config file) or before running the
test case (in the config file in the work directory).
cores¶
The number of cores (and the minimum) is proportional to the number of cells,
so that the number of cells per core is roughly constant. You can alter how
many cells are allocated to each core with goal_cells_per_core. You can
control the maximum number of cells that are allowed to be placed on a single
core (before the test case will fail) with max_cells_per_core. If there
aren’t enough processors to handle the finest resolution, you will see that
the step (and therefore the test case) has failed.
horizontal_advection¶
The horizontal_advection test case implements horizontal advection in a
constant velocity field of a Gaussian tracer. The domain is periodic in both
x and y, and the flow field is designed to return the tracer to its original
location at the center of the domain in 24 hours. The time step is
proportional to the grid-cell size.
By default, the resolution is varied from 2 km to 32 km by powers of 2.
The result of the analysis step of the test case is a plot like the
following showing convergence as a function of the number of cells:
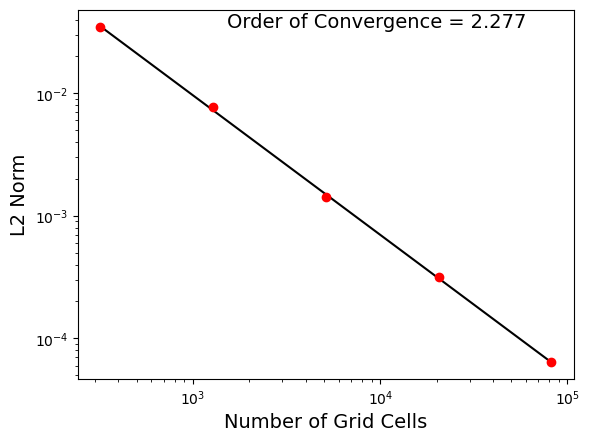
config options¶
The horizontal_advection config options include:
# options for planar horizontal advection test case
[horizontal_advection]
# Temperature (deg C) of the ocean
temperature = 15.0
# Salinity (PSU) of the surface of the ocean
salinity = 35.0
# center of the tracer gaussian (km)
x_center = 0.
y_center = 0.
# width of gaussian tracer "blob" (km)
gaussian_width = 50
# whether to advect in x, y, or both
advect_x = True
advect_y = True
# convergence threshold below which the test fails
conv_thresh = 1.9
# Convergence rate above which a warning is issued
conv_max = 2.3
The x_center, y_center and gaussian_width are used to control
properties of the Gaussian tracer. temperature and salinity are
constant background properties.